Bluetooth technology has become ubiquitous in the realm of wireless communication, and at the heart of its functionality lies the Bluetooth protocol stack. This article provides an in-depth look at the layers of the Bluetooth protocol stack, explaining how they work together to enable seamless device communication.
The Foundation: The Bluetooth Protocol Stack Overview
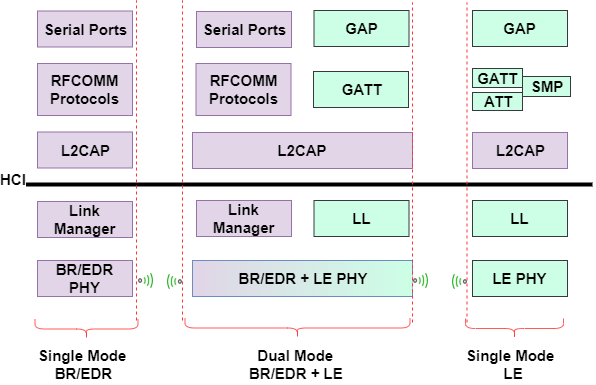
The Bluetooth protocol stack is a set of communication protocols that govern how Bluetooth devices interact with each other. It is built upon the OSI model and consists of several layers, each with a specific function, ranging from radio transmission to application support.
Layer 1: Radio Layer
At the base, the radio layer handles the transmission and reception of radio frequency signals. It is responsible for tasks such as frequency hopping, modulation, and signal encoding, ensuring reliable wireless communication.
Layer 2: Baseband Layer
The baseband layer manages the link between devices, controlling packet transmission, error handling, and data rate adaptation. It also handles device discovery and connection establishment, forming the basis for device pairing.
Layer 3: Link Manager Protocol (LMP)
The LMP layer is responsible for link management functions, including link setup, configuration, and termination. It also negotiates link parameters such as encryption and power management settings.
Layer 4: Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP)
L2CAP extends the baseband and LMP functionalities by providing additional services such as segmentation and reassembly of data packets, quality of service provisions, and multiplexing, allowing for the efficient sharing of a single physical link among multiple logical channels.
Layer 5: Host Controller Interface (HCI)
HCI is the interface between the host and the Bluetooth controller. It facilitates the exchange of commands, events, and data between the application layer on the host and the lower layers in the controller.
Layer 6: Service Discovery Protocol (SDP)
SDP is used for service discovery, allowing devices to find out what services and capabilities are offered by other devices. It is instrumental in the initial stages of device interaction, enabling the browsing of available services.
Layer 7: Application Profile Layer
The application profile layer includes a set of protocols and procedures that define how specific applications use Bluetooth technology. Examples include the Hands-Free Profile (HFP) for wireless headsets and the Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP) for streaming high-quality audio.
Applications of the Bluetooth Protocol Stack
The Bluetooth protocol stack enables a wide range of applications, from wireless audio streaming and data transfer to device networking and IoT implementations. Its robust design ensures compatibility and interoperability across diverse devices and use cases.
Challenges in Bluetooth Protocol Stack Implementation
Implementing the Bluetooth protocol stack comes with challenges, such as ensuring security, managing device compatibility, and optimizing power consumption. Addressing these issues requires careful design and adherence to Bluetooth standards.
Strategies for Effective Bluetooth Protocol Stack Utilization
- Standards Compliance: Adhere to Bluetooth SIG standards to ensure compatibility and functionality across devices.
- Security Measures: Implement security protocols at various layers to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Power Management: Optimize power consumption by efficiently managing link parameters and sleep modes.
- Interoperability Testing: Regularly test devices with a range of other Bluetooth devices to ensure seamless interaction.
Conclusion
Understanding the Bluetooth protocol stack is crucial for developers and engineers looking to harness the power of Bluetooth technology. Each layer contributes to the overall functionality, security, and reliability of Bluetooth communications. By demystifying the stack’s components and adhering to best practices, professionals can create innovative Bluetooth-enabled products that enhance connectivity and enrich user experiences. As Bluetooth technology continues to evolve, so too will the sophistication and capabilities of its protocol stack.
As a professional manufacturer of low power Bluetooth module, Tecksay has independently developed and produced a number of BLE Bluetooth modules that have been applied to many industries. With more than ten years of industry experience, Tecksay can customize BLE embedded solutions for customers from design, project management, function customization, system development and other aspects.