In the vast expanse of the Internet of Things (IoT), Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has emerged as a pivotal technology, weaving together a tapestry of interconnected devices. At the heart of BLE’s functionality lies the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT), which orchestrates the symphony of data exchange. Within this framework, Characteristics are the melodic notes that carry the essence of communication. This article delves into the role and intricacies of BLE Characteristics, exploring their structure, properties, and the vital role they play in IoT ecosystems.
The Essence of BLE Characteristics
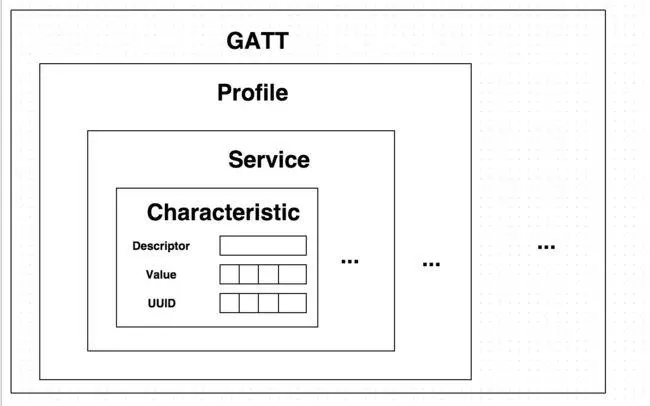
BLE Characteristics are the fundamental building blocks of GATT, representing the smallest unit of data that can be accessed, read, or written. They are the conduits through which devices exchange information, and their versatility is key to the dynamic nature of BLE technology.
Each characteristic is defined by a unique UUID (Universally Unique Identifier), which serves as its digital fingerprint, ensuring that it can be consistently identified across different devices and platforms. This standardization allows for a level of interoperability that is crucial for the diverse landscape of IoT devices.
Characteristic Properties
Characteristics in BLE are not mere data containers; they possess properties that define their behavior and the type of access they allow. These properties are akin to the genes of a characteristic, influencing how it interacts with the world.
- Read: This property allows a client device to retrieve the value of a characteristic from a server device. It’s the simplest form of interaction, akin to listening to a broadcast.
- Write: Enabling a client to overwrite the value of a characteristic, the Write property is the characteristic’s pen, allowing for the alteration of data.
- Write Without Response: A faster version of the Write property, it foregoes the need for an acknowledgment after a write operation, making it suitable for time-sensitive data.
- Notify: This property allows a server to send updates to a client without the need for constant polling. It’s like a subscription service, where the client receives notifications of changes.
- Indicate: Similar to Notify, but it requires an acknowledgment from the client, making it a more reliable form of communication, akin to a signed contract.
- Broadcast: A unidirectional communication method where the server broadcasts the characteristic value to all nearby clients, regardless of whether they’ve subscribed.
The Client Characteristic Configuration Descriptor (CCCD)
Central to the operation of Notify and Indicate properties is the CCCD. This descriptor, a special type of attribute, controls the server-initiated updates for a characteristic. It’s the switch that toggles the flow of information, determining whether a client will receive notifications or indications.
Discovering Characteristics
The process of discovering characteristics is akin to exploring a new world. When a BLE device connects to another, it embarks on a journey of discovery, seeking out the services and characteristics that define the other device’s capabilities. This is achieved through a series of ATT (Attribute Protocol) transactions, where the client queries the server for its attributes.
Data Types and Formats
Characteristics can encapsulate a wide array of data types, from simple integers and floating-point numbers to more complex structures like arrays or even strings. The format of the data is defined by the characteristic’s UUID, and understanding this format is crucial for interpreting the data correctly.
Security Considerations
In the world of IoT, security is paramount. BLE characteristics can be secured through various mechanisms, including encryption and authentication. Access to sensitive characteristics can be restricted based on the security mode of the connection, ensuring that only authorized devices can read or write to them.
Applications and Use Cases
BLE characteristics are the workhorses of IoT applications, enabling a wide range of use cases. From fitness trackers that update heart rate measurements in real-time to smart home devices that control lighting and temperature, characteristics are the silent heroes behind the scenes.
The Future of BLE Characteristics
As BLE technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of characteristics. With the advent of new standards and protocols, we can expect to see even more sophisticated data types and properties, further expanding the potential of IoT devices.
Conclusion
BLE Characteristics are the unsung heroes of the IoT world, quietly facilitating the exchange of data that powers our connected lives. Their versatility, combined with the robust framework of GATT, ensures that BLE remains a vital force in the ever-expanding realm of IoT. As we continue to innovate and push the boundaries of what’s possible, BLE characteristics will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping the future of wireless communication.