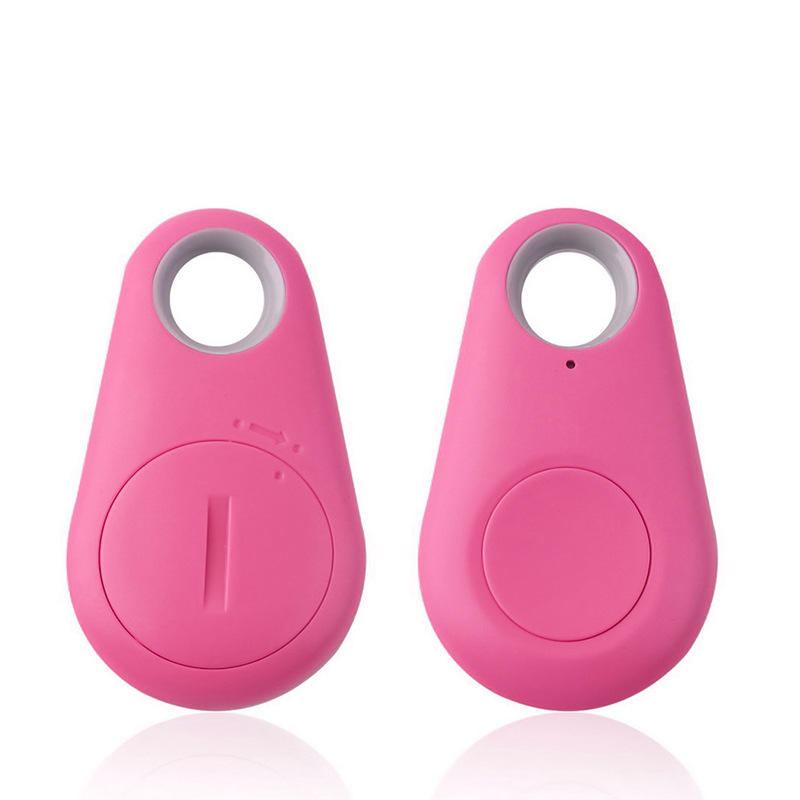
Bluetooth Low Energy beacons represent a class of compact wireless devices designed to emit signals to nearby portable electronics, facilitating precise location tracking and proximity sensing. These beacons have gained significant traction in recent years, attributed to their affordability and low energy consumption.
At its heart, a Bluetooth Low Energy beacon is composed of a microcontroller, a Bluetooth low energy radio module, and a battery, all neatly enclosed within a compact plastic casing. It routinely broadcasts distinctive identifiers, supplemented by optional data payloads, via Bluetooth’s advertising channels. Proximity to the beacon is ascertained by nearby devices that listen for these signals, gauging the signal’s strength to estimate distance.
A pivotal distinction of Bluetooth Low Energy beacons is their capacity to function autonomously, eschewing the need for traditional Bluetooth pairing processes with receiving devices. They emit signals in regular intervals, usually ranging from once every second to ten times per second. The receiving device’s measurement of signal intensity provides an approximation of its distance from the beacon, thereby enabling a suite of proximity-based functionalities.
To illustrate, a retail establishment might implement Bluetooth Low Energy beacons throughout the store. When a patron’s smartphone encounters signals from these beacons, it can initiate the delivery of location-specific content, such as discount offers or detailed product information. Bluetooth Low Energy beacons also serve to augment navigation and location services, supporting indoor mapping solutions or assisting users in finding misplaced items equipped with mini Bluetooth Low Energy tags.
Bluetooth Low Energy beacons present distinct advantages over other location-determining technologies like GPS or Wi-Fi. They are cost-effective, offer extended battery life, operate effectively indoors, and do not depend on pre-existing infrastructure. The streamlined Bluetooth Low Energy protocol is inherently power-frugal, rendering it exceptionally well-suited for deployment in devices powered by small batteries.
Nevertheless, Bluetooth Low Energy beacons are not without their constraints. They generally have an indoor operational range of 30-50 meters, which is more limited compared to other wireless technologies. Their signals are susceptible to interference and obstructions. Additionally, support for Bluetooth Low Energy beacons can differ across various mobile operating systems and hardware configurations.
In summary, Bluetooth Low Energy beacon technology delivers an efficient and cost-effective solution for applications centered around proximity detection, indoor navigation, and context awareness. As adoption continues to grow, these beacons are poised to become a ubiquitous tool for location-based services. Their straightforward broadcasting mechanism and minimal power consumption unlock a realm of opportunities in the burgeoning Internet of Things landscape.