BLE beacons are transforming fields like proximity marketing, indoor navigation, and asset tracking by facilitating smooth interactions with nearby devices. At the heart of their functionality are Bluetooth channels, which are vital for the dependable dispatch of signals. This article will explore what BLE beacon channels entail, their operational mechanism, and their significance for the beacon’s performance.
Understanding BLE Beacon Channels:
Operating within the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) protocol, BLE beacons utilize a frequency spectrum that is segmented into several channels. These channels act as conduits for data transmission between devices. For BLE beacons, they serve to emit signals with unique identifiers to devices in their vicinity.
Operation of BLE Beacon Channels:
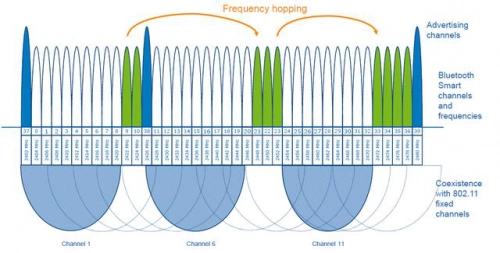
BLE beacons function across three advertising channels within the BLE spectrum: channels 37, 38, and 39. These channels belong to the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band, which is shared with technologies like Wi-Fi.
Upon activation, a BLE beacon starts broadcasting its unique identifier (UUID) and pertinent data on one of the advertising channels. It sequentially rotates through each channel, emitting its signal briefly before switching to the next. This rotation maximizes the beacon’s detection probability by broadcasting across different channels.
Significance of BLE Beacon Channels:
- Minimized Interference: Using multiple channels helps BLE beacons to reduce interference from other wireless devices in the same frequency band, ensuring reliable signal transmission even in congested areas.
- Enhanced Reliability: The use of multiple channels provides a fail-safe for beacon signals. Should one channel suffer from interference, devices can detect the signal on alternative channels, maintaining connectivity and ensuring that actions triggered by the beacon are executed correctly.
- Wider Coverage: Broadcasting across multiple channels expands the reach of BLE beacons, allowing them to communicate with a larger number of nearby devices. This is particularly useful for services that rely on smartphones and tablets, such as indoor navigation and proximity marketing.
- Dynamic Adaptation: BLE beacon channels allow beacons to adjust to varying conditions, maintaining communication reliability even when faced with wireless interference or signal loss.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to the BLE spectrum and channel allocation ensures that BLE beacons meet regulatory standards. By operating within designated channels, beacons prevent conflicts with other wireless services and adhere to regional regulations.
In summary, Bluetooth beacon channels are crucial for the reliable operation and performance of BLE beacons. Broadcasting on various channels within the BLE spectrum minimizes interference, boosts reliability, and broadens coverage, which is essential for effective marketing, navigation, and tracking applications. Recognizing the importance of BLE beacon channels is key to effectively deploying beacons and leveraging their full potential in proximity-based applications. As technology advances, BLE beacon channels will continue to be fundamental to the uninterrupted communication between beacons and devices, fostering advancements in location-based services and enriching user experiences.